GLAN THOMPSON BEAM SPLITTING
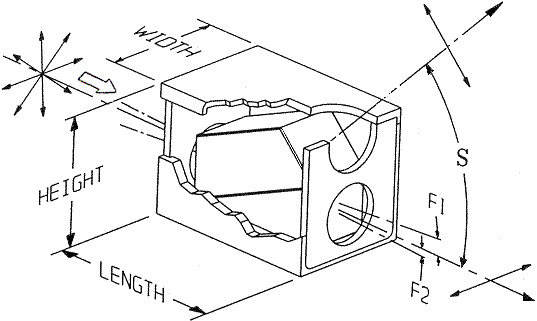
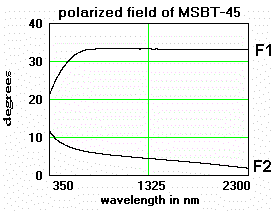
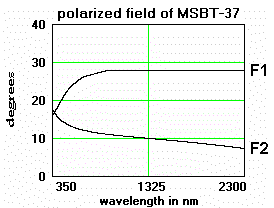
Specifications:
B grade calcite: greater than one wave wavefront deformation @ 633 nm due to striae only
A grade calcite: quarter to one wave wavefront deformation @ 633 nm due to striae only
S grade calcite: quarter wave wavefront deformation @ 633 nm due to striae only
Surface flatness: at least quarter wave @ 633 nm over the clear aperture
Surface quality: 40-20 scratch dig
Transmission (uncoated): 35-40% at 350 nm, 65-70% at 400 nm, 80-88% at > 500 nm
please visit Anti Reflection Coating page for reflectivity plots of available coatings
Calcite is a natural mined crystal. Defects in bulk calcite are characterized by bubbles (presence of randomly scattered bubbles vary from relatively large to small sizes and fine bubble lines), striae (streaks of sudden variation of refractive index which can be detected interferometrically), optical inhomogeneity (gradual variation of refractive index in bulk material) and stress birefringence (variation of birefringence in bulk material due to defective growth of the crystal). These defects cause degradation of polarization and transmission loss due to scattering and absorption.
|
BEAM SPLITTING GLAN THOMPSON |
|
Catalog Number |
Clear Aperture Diameter (mm) |
Mount Dimensions (Inches) |
Remarks | ||
|
Height Maximum |
Width +/- .0025 |
Length +/- .005 |
|||
| MSBTB- 8-45 | 8 | .875 | .622 | 1.125 |
Grade B Extinction - Reflected Beam 1*10^-4 Extinction - Straight Through Beam 5*10^-5 |
| MSBTB-10-45 | 10 | 1.000 | .872 | 1.375 | |
| MSBTB-12-45 | 12 | 1.125 | .996 | 1.500 | |
| MSBTA- 8-45 | 8 | .875 | .622 | 1.125 |
Grade A Extinction - Reflected Beam 5*10^-5 Extinction - Straight Through Beam 1*10^-5 |
| MSBTA-10-45 | 10 | 1.000 | .872 | 1.375 | |
| MSBTA-12-45 | 12 | 1.125 | .996 | 1.500 | |
| MSBTS- 8-45 | 8 | .875 | .622 | 1.125 |
Grade S Extinction - Reflected Beam 1*10^-5 Extinction - Straight Through Beam 5*10^-6 |
| MSBTS-10-45 | 10 | 1.000 | .872 | 1.375 | |
| MSBTS-12-45 | 12 | 1.125 | .996 | 1.500 | |
| MSBTB- 8-37 | 8 | .875 | .622 | 1.500 |
Grade B Extinction - Reflected Beam 1*10^-4 Extinction - Straight Through Beam 5*10^-5 |
| MSBTB-10-37 | 10 | 1.000 | .872 | 1.625 | |
| MSBTB-12-37 | 12 | 1.125 | .996 | 1.875 | |
| MSBTA- 8-37 | 8 | .875 | .622 | 1.500 |
Grade A Extinction - Reflected Beam 5*10^-5 Extinction - Straight Through Beam 1*10^-5 |
| MSBTA-10-37 | 10 | 1.000 | .872 | 1.625 | |
| MSBTS-12-37 | 12 | 1.125 | .996 | 1.875 | |
| MSBTS- 8-37 | 8 | .875 | .622 | 1.500 |
Grade S Extinction - Reflected Beam 1*10^-5 Extinction - Straight Through Beam 5*10^-6 |
| MSBTS-10-37 | 10 | 1.000 | .872 | 1.625 | |
| MSBTS-12-37 | 12 | 1.125 | .996 | 1.875 | |
